Long-term exposure to sound may lead to damages and even losses in the auditory system. That is why the European directive 2003/10/CE dictates that sound exposure in the workplace should be regulated [1]. The French Law reflects this in the article R4431-2 in their Labor Code [2], which indicates the maximum sound pressure levels for acoustic shocks, as well as for the average exposition in an 8-hour working day. Without taking any preventive actions, these limits are 135 dB(C) and 80 dB(A), respectively [2] [3].

This becomes a significant problem for people in call centers, for example, where sound exposition is constant and numerous headsets do not comply with EU regulations. In addition, some manufacturers may present data that does not reflect the actual response evolution during a complete working day. It is therefore necessary to be able to characterize these headphones in order to comply with the law.
ARTEAC-Lab tackles this issue by performing acoustic measurements on the headsets by means of an artificial head and an ear simulator, according to the ITU-T P.64 and ITU-T P.57 recommendations. Then, as per ISO 11904-2 [4], the level at the center of the listener’s head is converted into its corresponding diffuse field equivalent [3],[4].
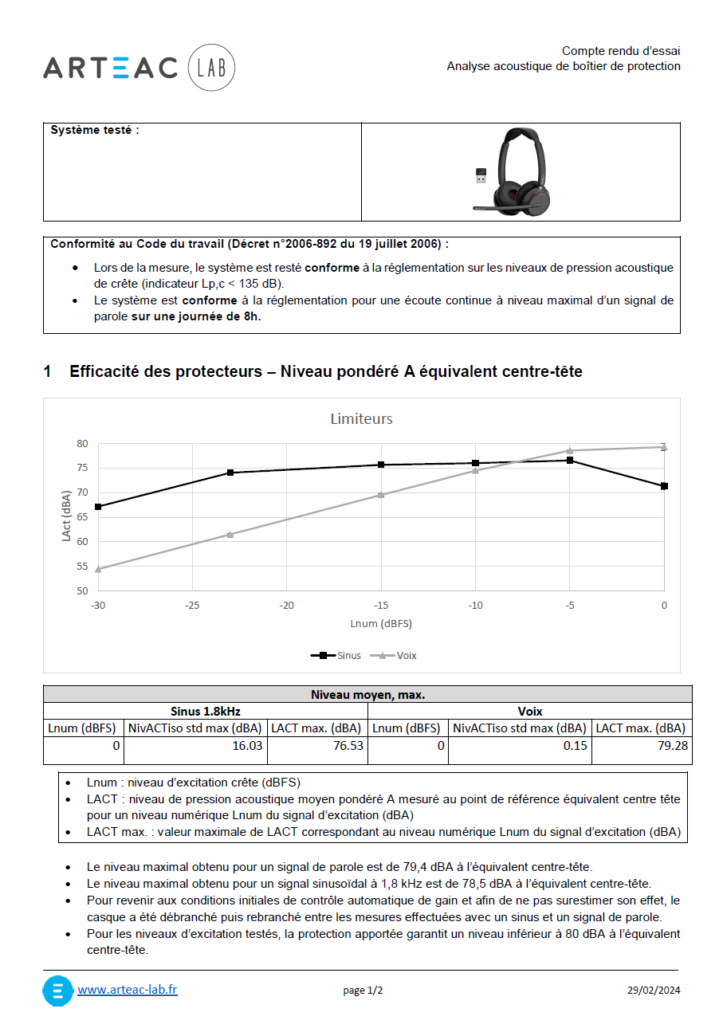
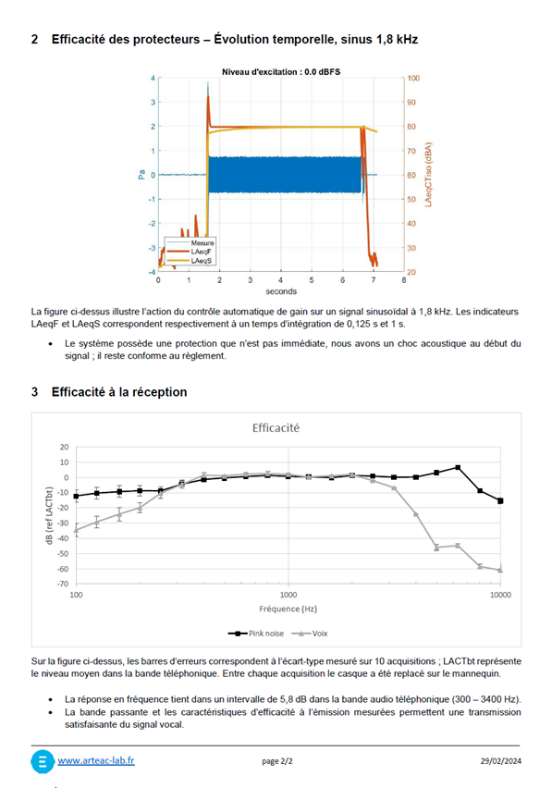
By evaluating not only the efficiency of the protections and limiters but also the temporal evolution of both sinusoidal and vocal signals, it is possible to effectively ensure the performance of the headphones and their compliance with regulations. Arteac-Lab is working on these issues with EDF, a company at the forefront of ensuring workplace safety for its employees.
References:
- [1] DIRECTIVE 2003/10/CE DU PARLEMENT EUROPÉEN ET DU CONSEIL, 2003)
- [2] Code de Travail, 2008 , Article R4431-2. France
- [3] Trompette, N., & Chatillon, J. (2010). Evaluation des risques pour l’audition des opérateurs des centres d’appels téléphoniques et solutions de prévention. INRS
- [4] ISO 11904-2:2021. (2021, February). Acoustics — Determination of sound immission from sound sources placed close to the ear. Part 2: Technique using a manikin.

